Published: Mar 1986 | Env. Health Perspectives. 1986;65:351-361.
Indirect health effects of relative humidity in indoor environments
Arundel A.V., Sterling E.M., Biggin J.H., Sterling T.D.
Abstract
The review focusses on direct and indirect effects on human health. Direct effects are related to comfort aspects and impacts on the physiology of human organs especially airways mucous membranes (including immune defence mechanisms), skin, eyes and other organs.
Indirect effects include all consequences of changing humidity levels on microbes (viruses, bacteria, fungi), allergens, air quality (particles, physical and chemical reactions), elimination rate of airborne pathogens and possible harmful consequences of contaminated humidifiers.
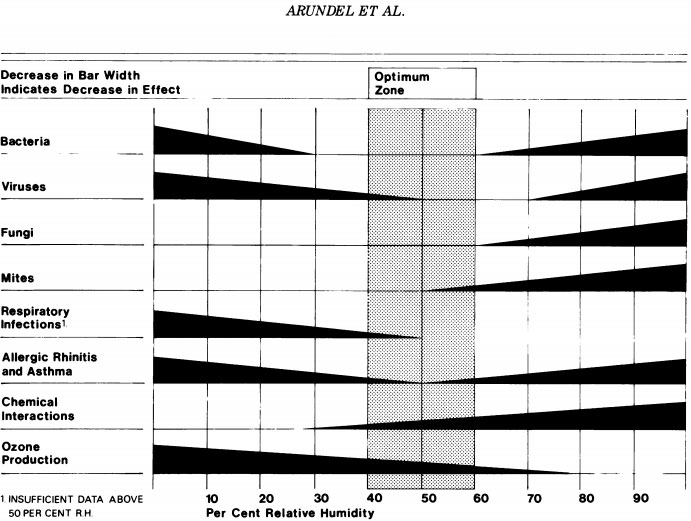
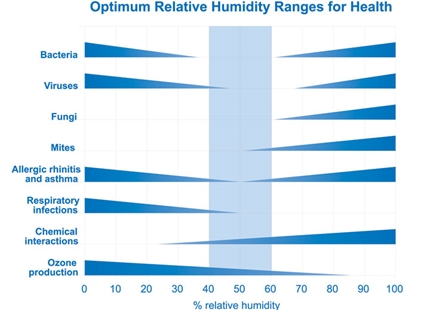
A large body of literature on health effects of relative humidity in indoor environments suggests that relative humidity can affect the incidence of respiratory infections and allergies. Experimental studies on airborne-transmitted infectious bacteria and viruses have shown that the survival or infectivity of these organisms is minimized by exposure to relative humidity between 40 and 70%.
Nine epidemiological studies examined the relationship between the number of respiratory infections or absenteeism and the relative humidity of the office, residence, or school. The incidence of absenteeism or respiratory infections was found to be lower among people working or living in environments with mid-range versus low or high relative humidity.
Most species of fungi cannot grow unless the relative humidity exceeds 60%. Relative humidity also affects the rate of off gassing of formaldehyde from indoor building materials, the rate of formation of acids and salts from Sulphur and nitrogen dioxide, and the rate of ozone formation.
The influence of relative humidity on the abundance of allergens, pathogens, and noxious chemicals suggests that indoor relative humidity levels should be considered as a factor of indoor air quality.
Conclusion
The majority of adverse health effects of low relative humidity can be minimized by maintaining indoor levels between 40 and 60%. This requires humidification during winter in areas with cold winter climates.
Humidification should preferably use evaporative or steam humidifiers, as cool mist humidifiers can disseminate aerosols contaminated with allergens, bacteria and fungi.

Dry air and airborne infection
Low humidity acts as a conduit for viruses and airborne bacteria to disperse and travel around a building and threaten all occupants.
Read moreDry air and our airway defence system
Low humidity dries our mucous membranes and inhibits our body's natural defence against airborne germs, viruses and bacteria.
Read moreDry air and our eyes
Low humidity dries our eyes' precorneal tear film making us prone to eye irritations and contact lens discomfort.
Read moreDry air and our skin
Low humidity dries the outer layer of our skin leading to itchiness, cracking and dermatological problems.
Read more